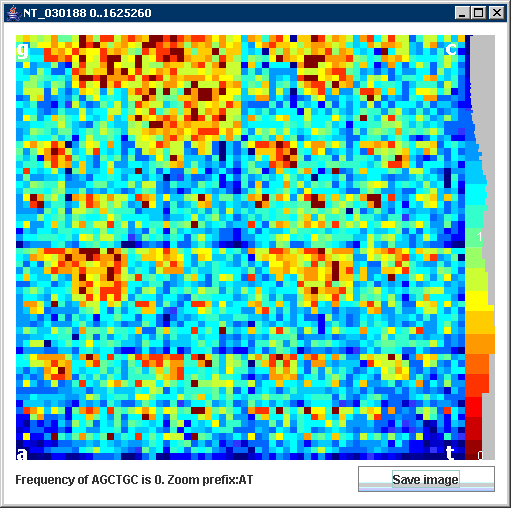
 Our JAVA program is a tool for visualization of large genomes by Chaos Game Representation CGR (Jeffrey 1990). CGR transforms DNA sequence to the colored image (figure on the right). Every pixel corresponds to a short sequence of n symbols called n-mer. Color of pixel reflects n-mer frequency in the analyzed sequence. This gives us histogram that allows seeing sparse and dense occurrences of n-mers quickly.
Our JAVA program is a tool for visualization of large genomes by Chaos Game Representation CGR (Jeffrey 1990). CGR transforms DNA sequence to the colored image (figure on the right). Every pixel corresponds to a short sequence of n symbols called n-mer. Color of pixel reflects n-mer frequency in the analyzed sequence. This gives us histogram that allows seeing sparse and dense occurrences of n-mers quickly.
Features
- Visualization - 2D histogram of n-mer frequency
- Region selection - user can choose any region in DNA sequence for visualization by specifying the start point and length of sequence
- Zoom - any part of image can be enlarged by single mouse click
- Memory selection - user can choose length of n-mers (from 4 to 10 symbols)
- Features selection - (only for .gb files) user can set region selection to cover exactly one feature (described in GenBank file) by clicking on the feature name
Installation
- Download ifs.zip, unzip file and execute java -jar IFS.jar.
- For large sequences you have to increase heap size for runtime enviroment with -Xmx parameter, e.g.: java -Xmx100M -jar IFS.jar for 100MB of memory.
- While it is very easy to download our tool, it requires having a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) installed on your system.
- Demo sequences: GenBank format, Fasta format.
Description
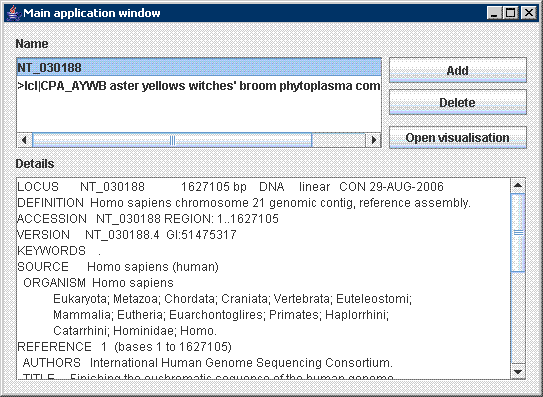
After initialization the tool prompts user to browse for an input file (in .fasta or .gb format) on the disc. Parameters of visualization are displayed immediately in a control window: Application works with genomic data in commonly used formats FASTA and GENEBANK. Sometimes GENEBANK format contains descriptive information about sequence such as sequence description, source, authors, references and specification of other features included in genome. These are extracted by program and used later in visualisation process. In the Main application window all opened sequences with their details are shown . Afterwards several visualisations windows can be opened and handled simultaneously. All available parameters of visualisation are shown in the Visualisation control window, which is used to interactively adjust visualisation.
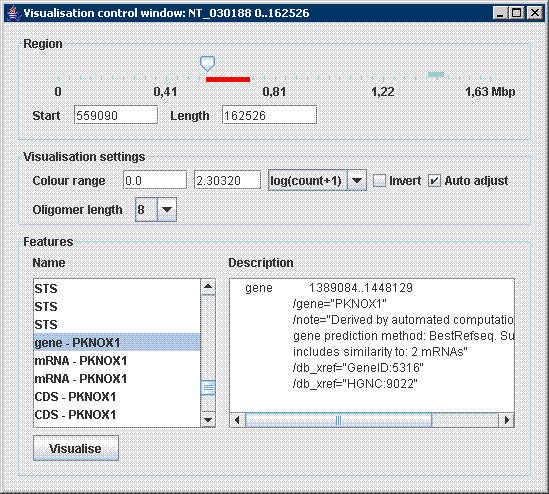
The main parameter of visualisation, i.e. region in genome employed in visualisation is controlled by slider in the top of the window. User can specify region directly by entering start position and length, or using slider control to move region swiftly through the genome. Actual position and length of region is displayed in slider control as a red bar with corresponding size.
GENEBANK format might include specification of genomic features such as genes, mRNA, etc. These are extracted from input file and listed in the Features part of window. After a user selects feature its description is displayed in the right part. The Visualise button can be used to visualise selected feature immediately. This allows us easily analyse important parts of genome simply by a single click.
Remaining parameters of visualisation are listed in section Visualisation settings. Colour range, i.e. transformation of oligomer frequency to colour heatmap can be adjusted. Minimum value is shown in blue and maximum in red colour. When automatic adjustment of colour range is chosen, maximum value is always recalculated to display the most frequent oligomer in red colour. Highlighting of oligomers with low and high frequency simultaneously can be achieved by logarithmic scale of colour heatmap, i.e. log(count) is applied to counter value.
Coloured heatmap can be inverted which is useful when looking for infrequent oligomers (right image). Number of cells in visualisation can be changed from 4x4 to 1024x1024 by choosing different oligomers lengths. Each visualisation is opened in a separate window which title displays sequence name and visualisation range. Heatmap on the left side is used to display both transformation of frequency to colour and histogram of colours used in the image. Histogram of colours makes setting up optimal parameters for colour transformation easier.
References
- H.J. Jeffrey, "Chaos game representation of gene structure", Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2163-70.
- Almeida JS, Carrico JA, Maretzek A, Noble PA, Fletcher M., "Analysis of genomic sequences by Chaos Game Representation", Bioinformatics. 2001 May;17(5):429-37.
- Shen J, Zhang S, Lee HC, Hao B, "SeeDNA: a visualization tool for K-string content of long DNA sequences and their randomized counterparts", Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2004 Aug;2(3):192-6.
Tool redistribution and citation policy
This tool is freely available to the public. The author Matej Makula gives permission for this product to be used without license for any purpose under the condition the author and this web page are clearly acknowledged as the source of the product.
Paper
Makula M. and Benuskova L. (2009) Interactive visualisation of oligomer frequency in DNA. In: Computing and Informatics, Vol. 28, 2009, 695–710 download
Contact
If you have any comments, questions or ideas for functionality improvement do not hesitate to contact me via .